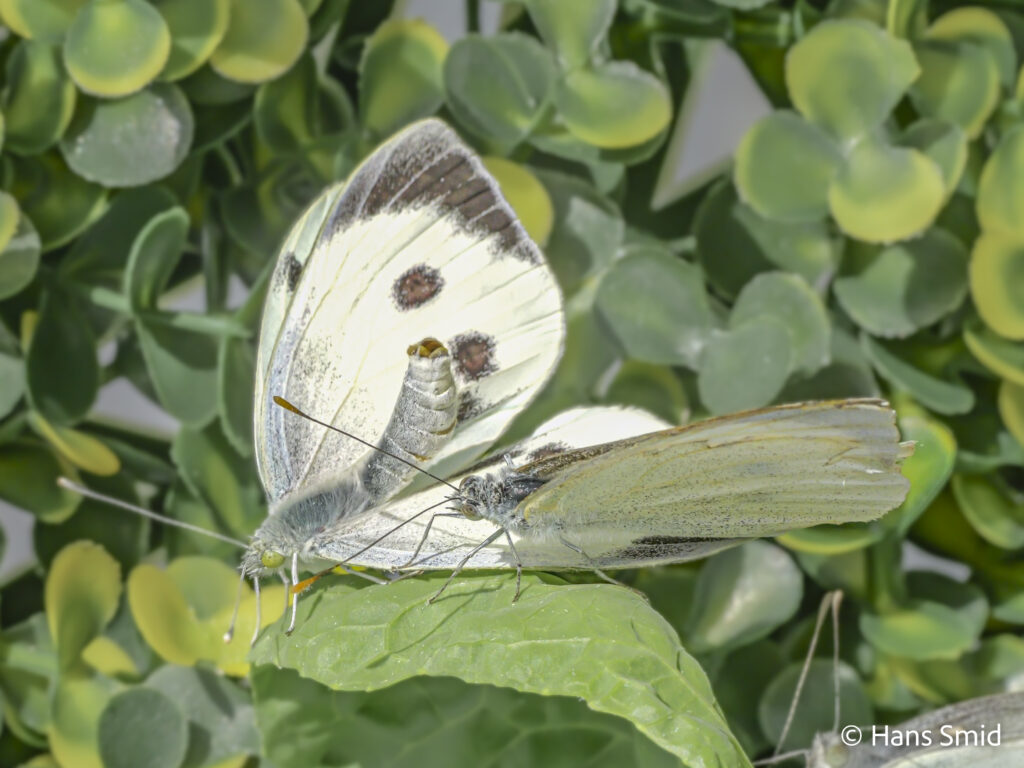
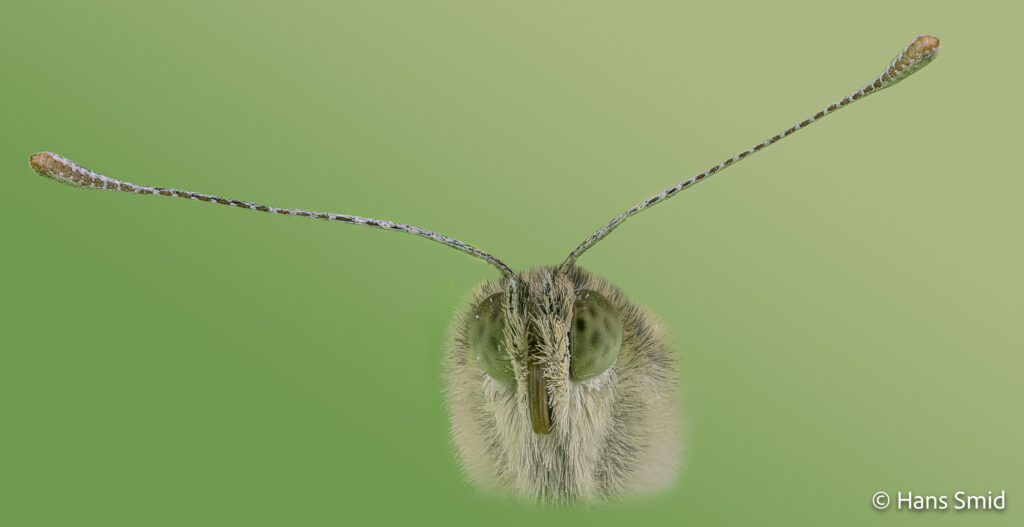
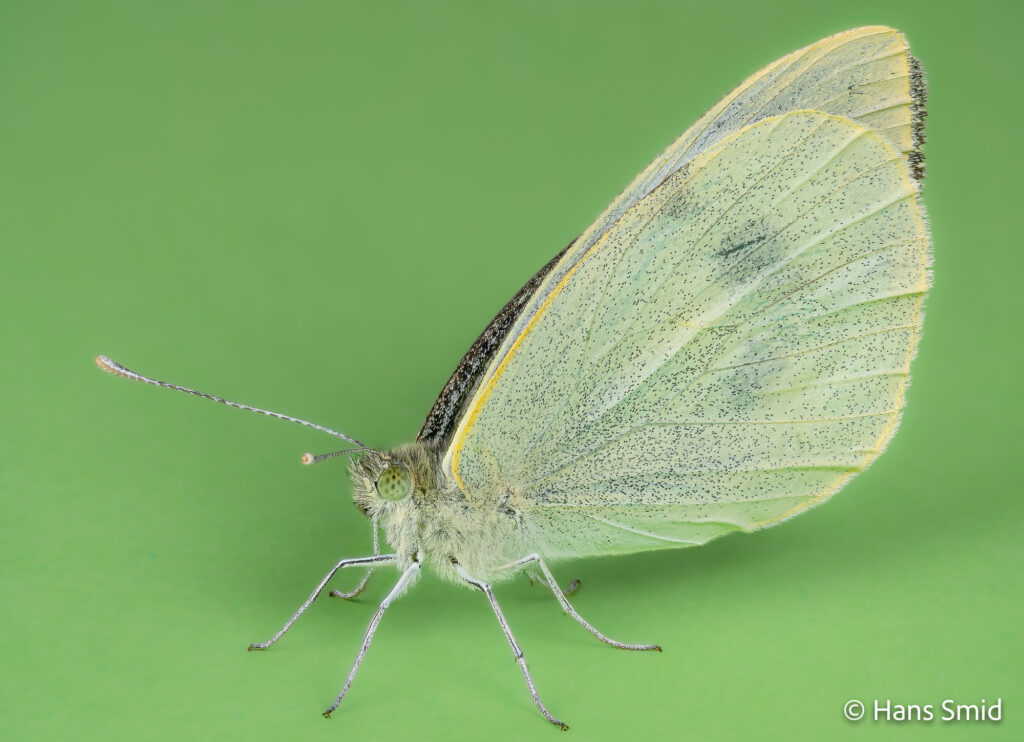
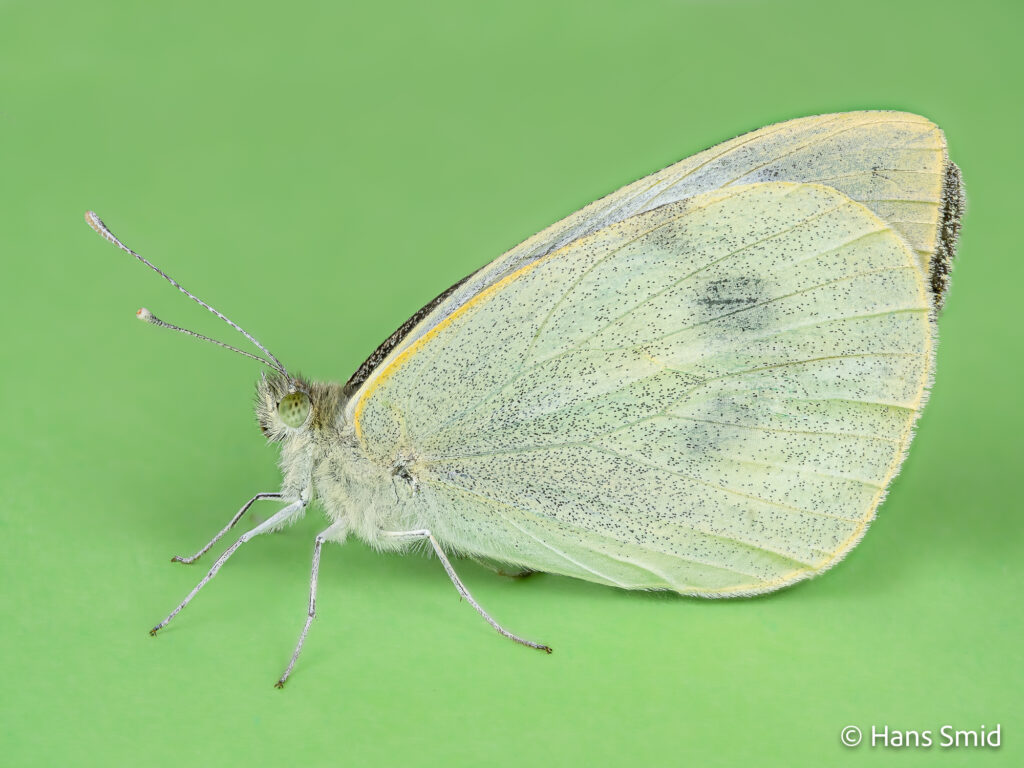
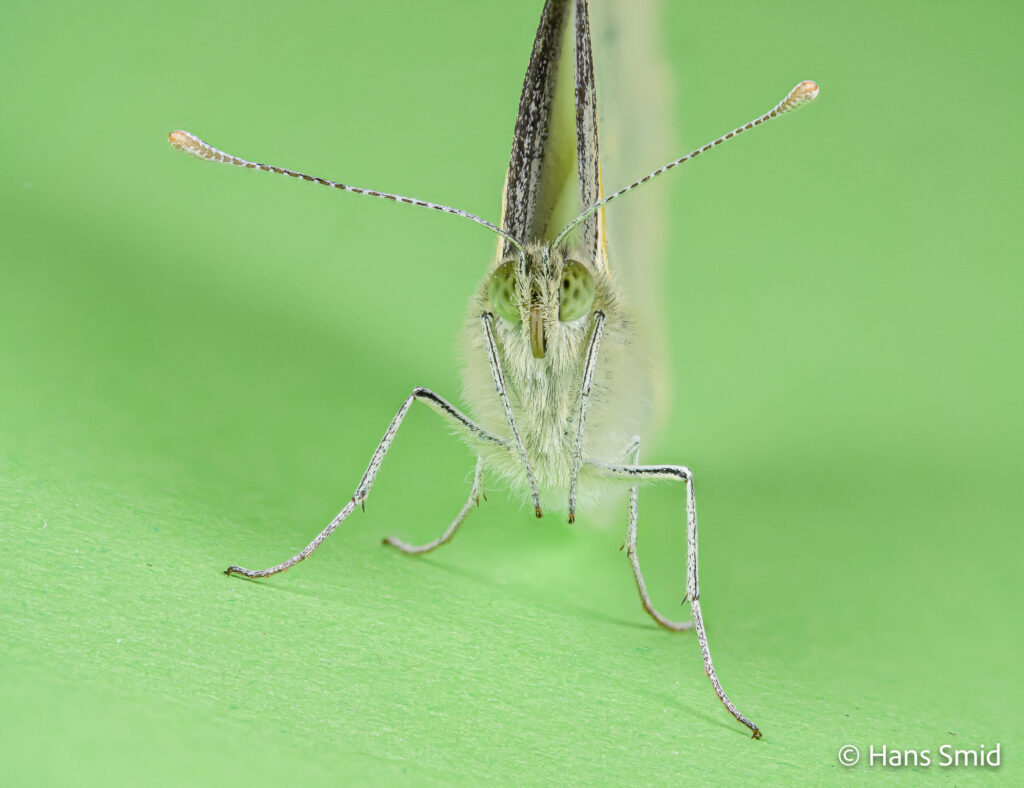
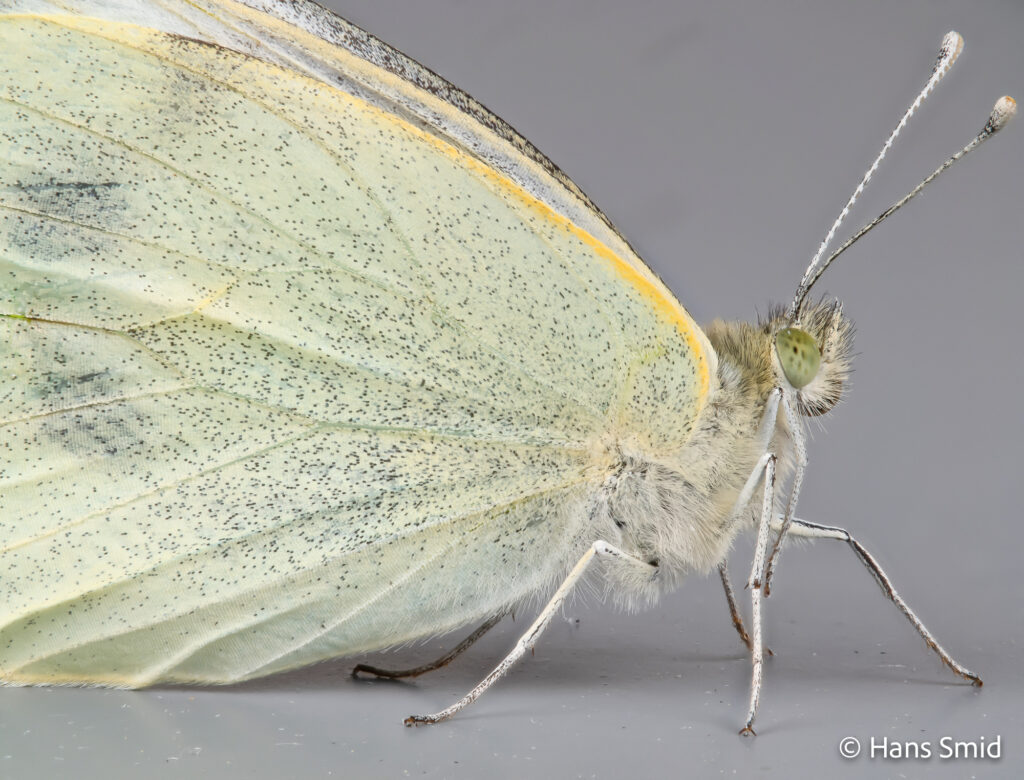
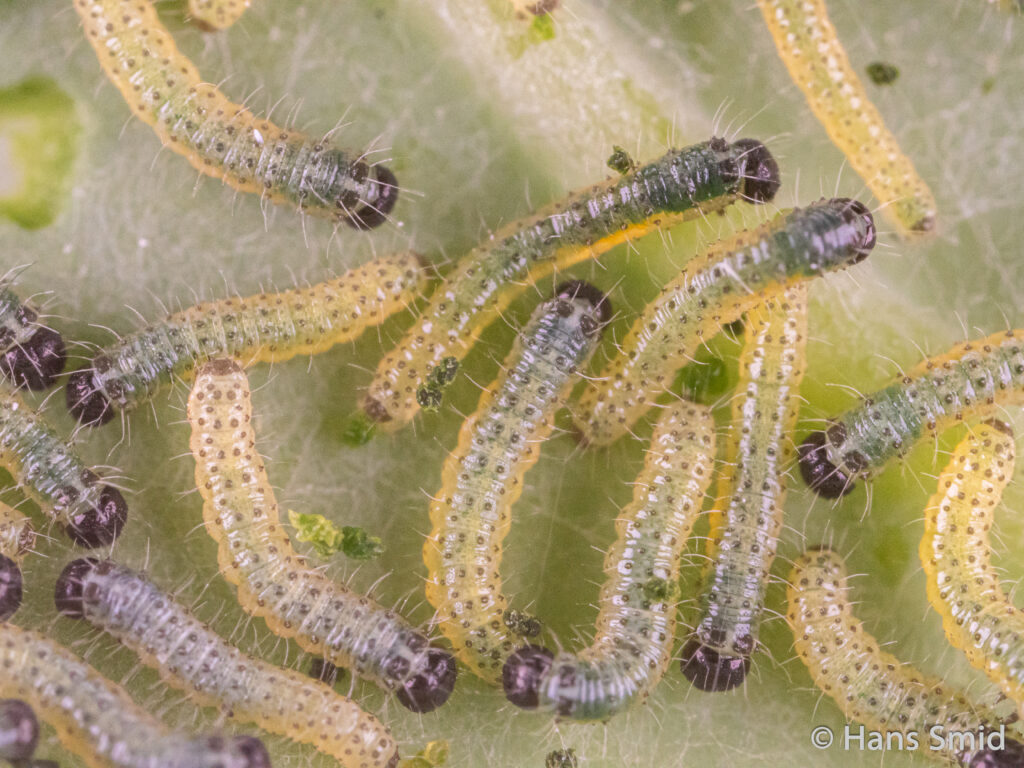
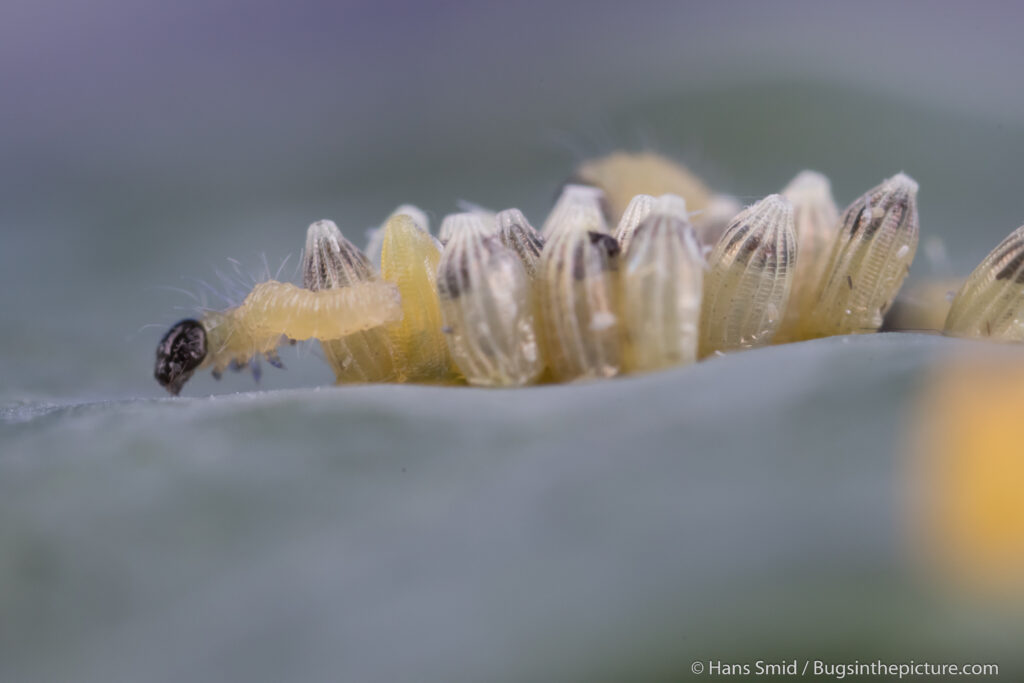
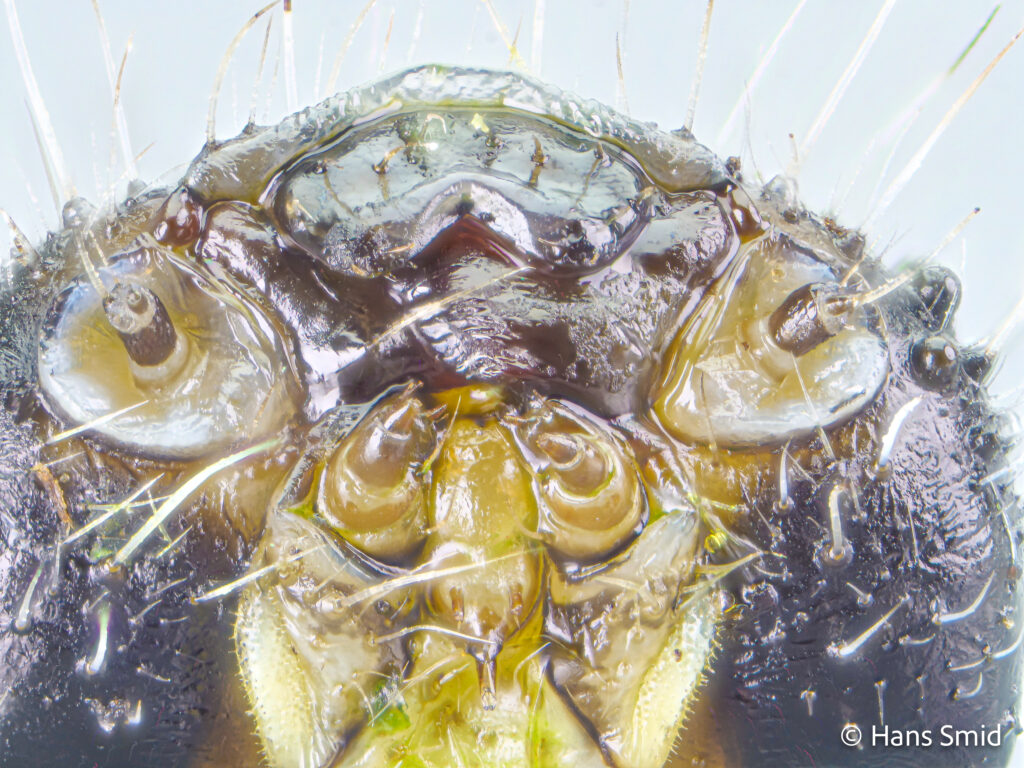
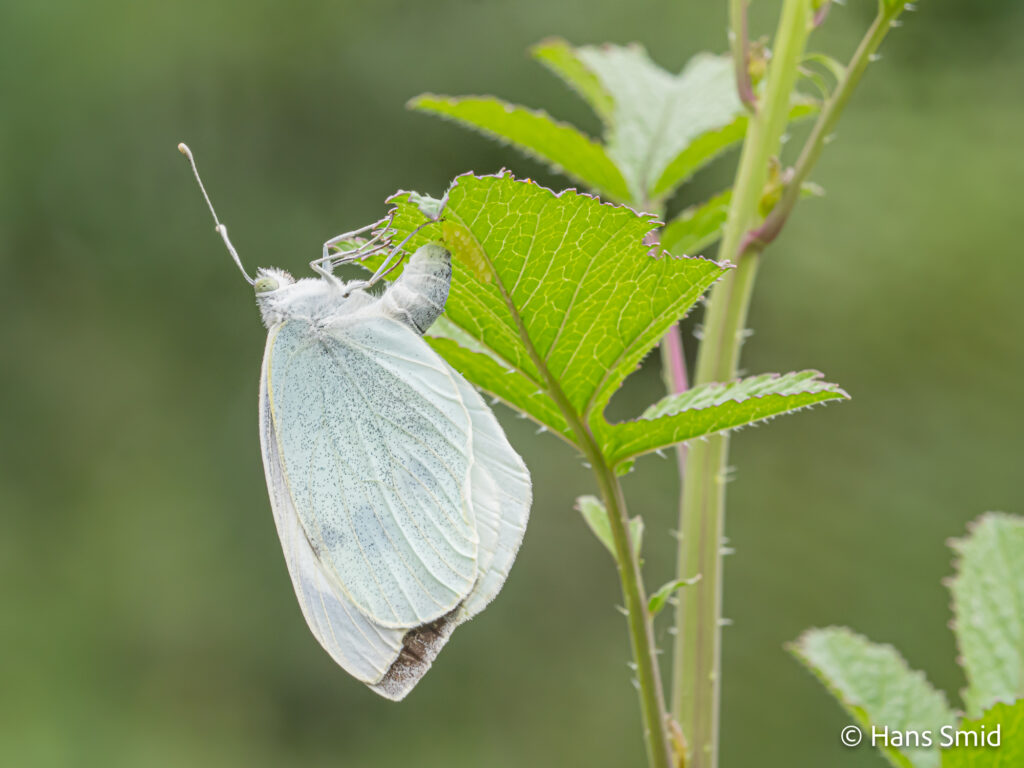
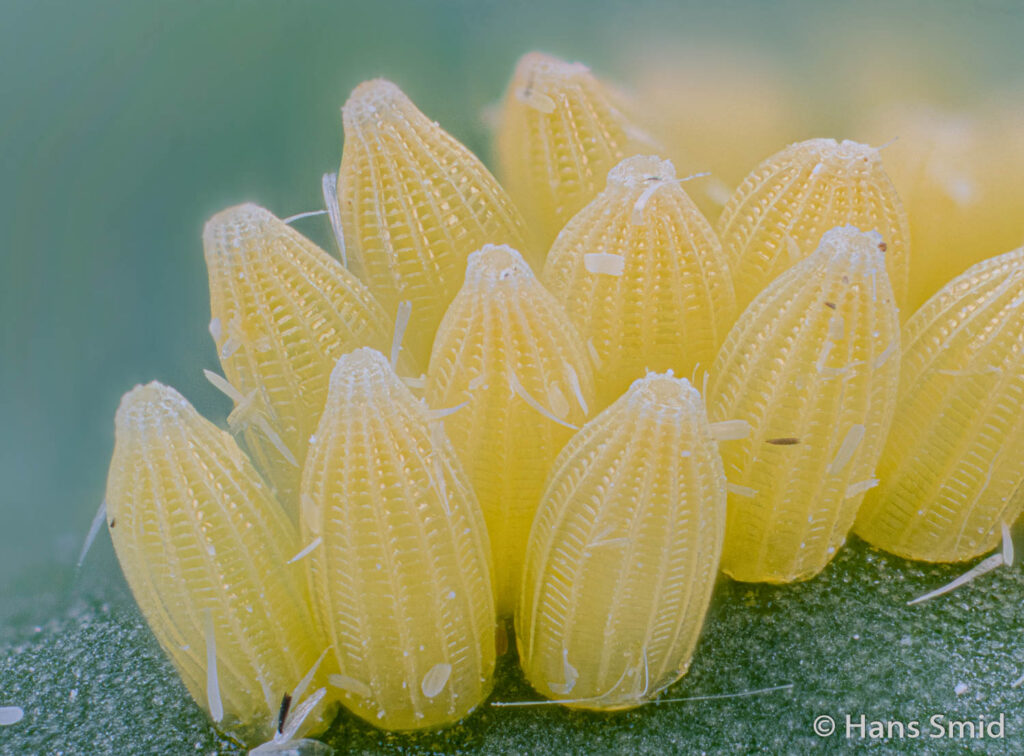
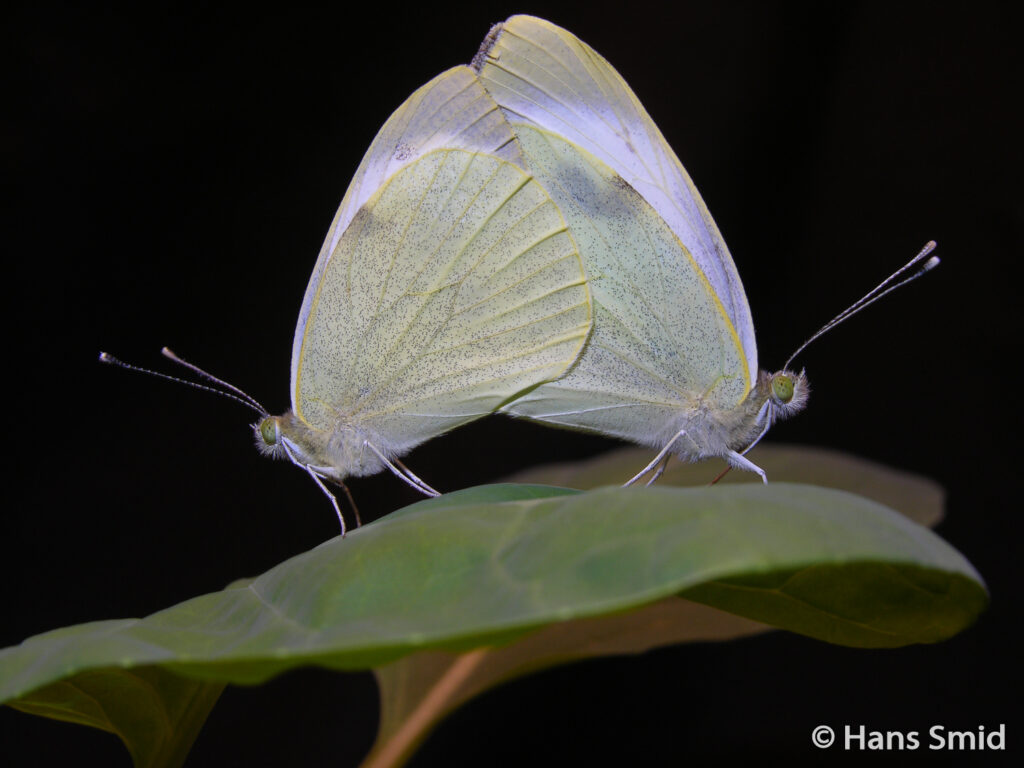
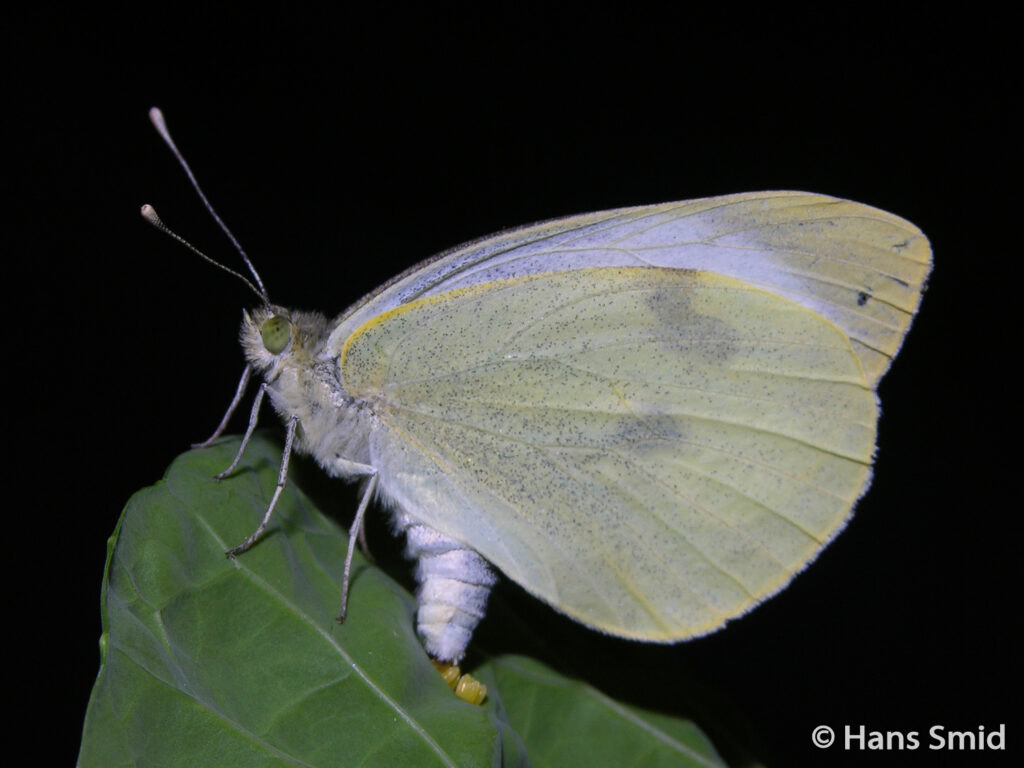
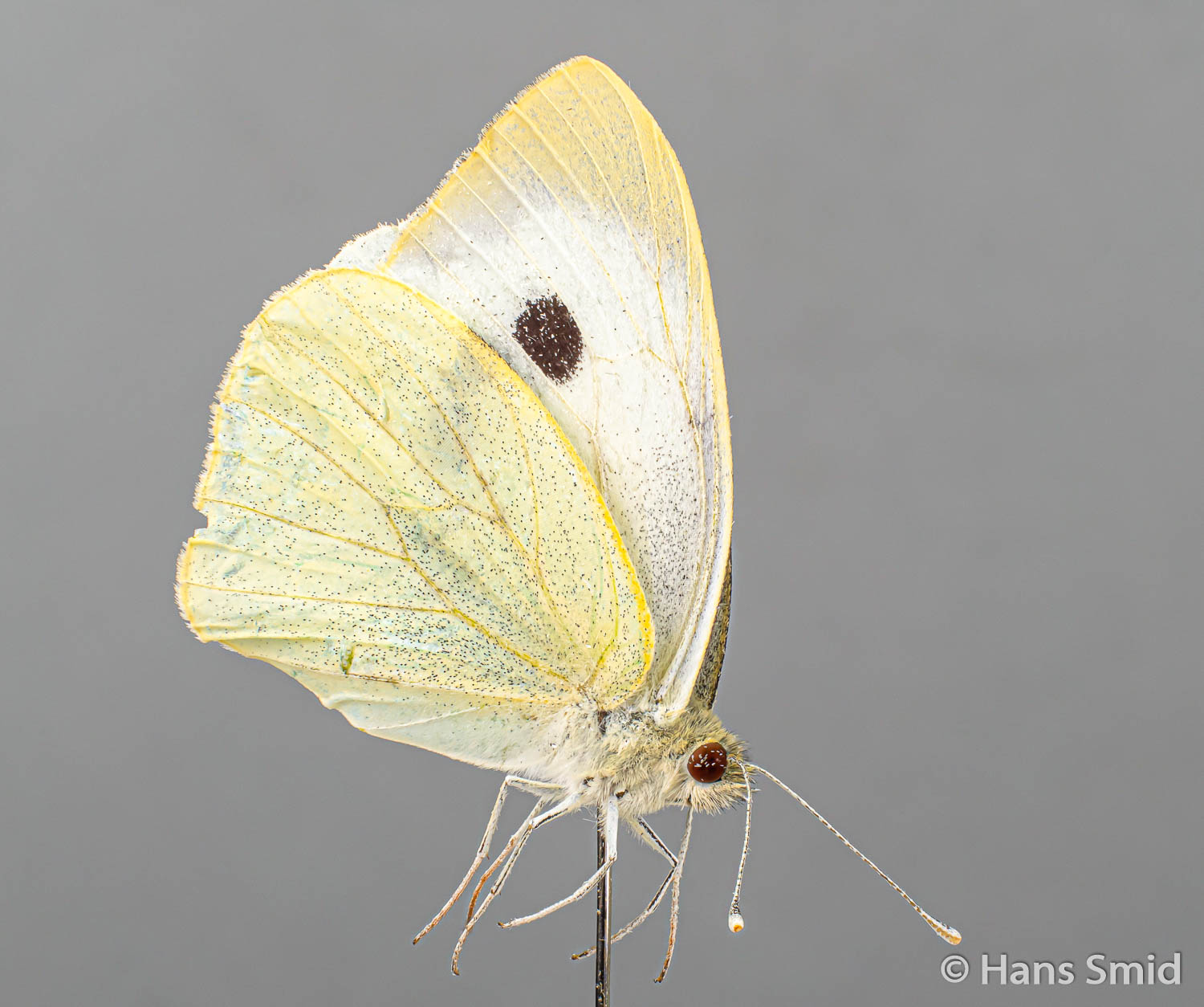
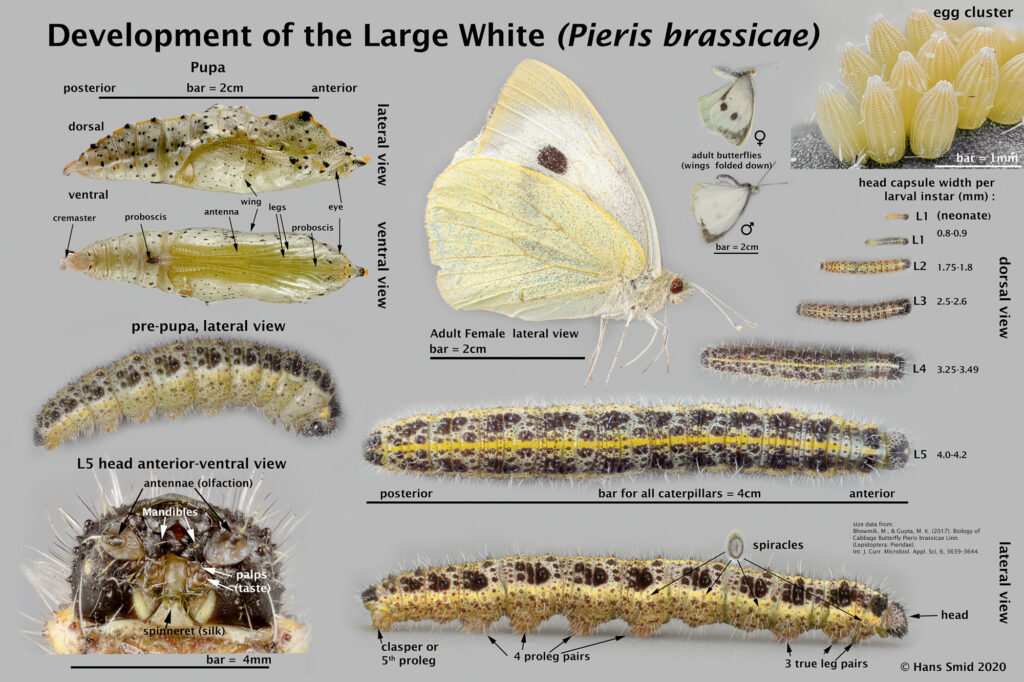
The large white butterfly lays here eggs on plants of the Brassicaceae family. The caterpillars are specialist feeders on these plants, which is why this species is often referred to as the large cabbage white. The eggs are laid as large clusters and there are five larval instars. The full life cycle can be found on this wall chart.
This video is not about butterflies foraging on flowers for nectar…. Whereas there is now ample attention for the need for flowers to support the declining numbers of insects, there is much less attention for the offspring of the butterflies, the caterpillars. Nectar is of course very important to support the survival of butterflies, but ultimately the female butterfly has to find a suitable host plant on which she can lay her eggs. This host plant is not necessarily a plant with abundant beautiful flowers, but it will support the growth of the caterpillars. In this video, you can see for example how the large cabbage white butterfly (Pieris brassicae) carefully lays her eggs, and glues them, one by one, underneath a leaf of a black mustard plant. There is an interval of about 30-60 seconds between each egg, and the butterfly lays several tens of eggs into a neat cluster. Needless to say that it is important for butterfly conservation to support host plants as much as nectar plants! The video is available in 4k resolution.